
Have you been hearing the term ‘Quaternion Rotations’ in Blender and wondered what they are -- or even how to control them?
What this article covers
So...what are quaternion rotations?
Quaternions are 3D rotations performed by the multiplication of quaternions.
Got it? Yeah, probably not...
Before explaining how these rotations work, we'll need to define a few terms first.
Before we begin...
1) In computers, everything is represented by numbers.
Numbers make up everything we do on computers (including Blender). Whether it is a character, an operation, the position of a pixel on your screen, a color... or even a number. Blender will see all operations and input as numbers.
2) Any point in 3d space has three coordinates
A single point P has coordinates x, y and z. For example, (3.0, 0.73, 2.5). But these coordinates can also represent a 3-dimensional vector.
A number in the form of a ‘triple’ (a, b, c) can represent a simple point, but it could also be another 'type'.
A 'type' refers to a point, but also a color, or a vector.
One type can even change into another, which is what we call 'type-switching'.
3) A triple can represent a vector type
You may remember vectors from high school maths: a vector is like an arrow, with a direction and a length, but not a fixed position.
In our example, vector (3.0, 0.73, 2.5) is an arrow going from the origin (0, 0, 0) to point (3.0, 0.73, 2.5).
It can be placed anywhere in 3D space, it is still considered the same vector, just with a different triple.

You can rotate or scale a vector and its coordinates will change accordingly.
Internally, Blender will see all these numbers as ‘triples’.
4) Blender uses triples to determine various operations
Knowing this, we can do some cool things like use a Vector output to drive the color of a shader.
And because everything is a number it’s also possible to do completely ridiculous and meaningless things: like determining the length of color. What!? A colour can have a length? Well a color to Blender is just a number and so yes, you can find the length of that number.
In this example I am taking the cross product of a point in space and a Noise Texture, and plugging the result into an emission shader. Did I mention you can do completely ridiculous things with numbers?

5) Quaternions = Hamilton numbers
In the rest of this article, I am going to do something outrageous and call quaternions ‘Hamilton numbers’. Firstly, I think this sounds more friendly, less intimidating. And secondly, this way you are less likely to forget that a quaternion is a number.
Understanding Complex Numbers (in 2D)
Hamilton numbers are the best way to rotate in 3d space - and we will get to them shortly, but for simplicity, first, let's look at 2D.
(Watch out: extreme ‘type-switching’ ahead!)
Let’s say we have a 2-dimensional plane, called 'real plane', with a point that we want to rotate around the Origin.
(If we can do that, we can rotate as many points as we like around any point on the plane.)
Now, we'll create a (linked) ‘copy’ of this plane and place it perpendicular to our real plane. The copy is called a 'complex plane' (for historical reasons, not because of its complexity! We might as well call it the relax plane...):
Everything that happens in the real plane also happens in the complex copy -- and vice versa.
 

For every point (a, b) on our real plane, there is a point on the complex plane.
This point represents a complex number (a+bi). The i portion of this is called an ‘imaginary number’, where i² = -1.
Quick recap: Now we've introduced complex numbers (points on our complex plane) and an imaginary number i.
Now, multiplying two points doesn’t make much sense, but we can easily multiply two numbers (even when they are ‘complex’).
Example 01 with complex numbers in 2d
For a point P(a, b) in our real plane, there is a corresponding point P(a+bi) in the complex plane.
If we multiply this point by i [this is the complex number (0+1i)], we get:
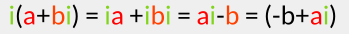

Now comes the beautiful part: if we look at this graphically, we can see that we just rotated the vector (a, b) by 90° (around the Origin):

There’s one thing to note about this example.
We multiplied our vector by i, which has a length of 1. That's because it is a vector that moves exactly 1 unit in a given direction.
If we would have multiplied by 2i, we still would have rotated 90°, but also scaled vector P by a factor 2.

There's another way of seeing this.
The same operation would be done if we multiplied two vectors by adding their angles and multiplying their lengths.
So we will make it a convention to only multiply by vectors of length 1, that is: by numbers, whose corresponding points lie on the unit circle. When we add the angles and multiply the length by 1, we will only get the rotation, without any scaling.
Example 02 with complex numbers in 2d
This works for any angle; we take the unit vector in the complex plane that makes the desired angle with the positive X-axis and multiply the corresponding number by the number belonging to the point we want to rotate. Put the result back into the real plane and Bob’s your uncle.

If we call the angle of rotation , we can also write point C as: (cos, sin) and the number as: (cos+isin). This will become especially useful in 3D.
If a number lies on the unit circle, meaning it corresponds to a vector of length 1, we say the number has a Norm 1. (As numbers do not have a length. This is the equivalent of length for vectors and distance (to origin) for points.)
Example 03 with complex numbers in 2d
Here is an important term:
if we have a complex number 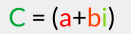 then we call
then we call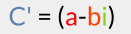 its complex conjugate.
its complex conjugate.
(Here I use the notation C' to indicate the conjugate of C, but there are other notations that you may encounter...)
When we multiply a complex number P by some complex number C of Norm 1, we rotate by a certain angle θ.
If we after that multiply again, but this time by the conjugate of C, we rotate by an angle of (360°-θ) and thereby return to the original place of P.

As a special case: if P is an imaginary number, meaning its real part is 0, for instance: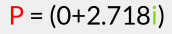 then
then  is also an imaginary number for any complex number C. Although this sounds trivial here, it will be extremely important when dealing with 3D rotations!
is also an imaginary number for any complex number C. Although this sounds trivial here, it will be extremely important when dealing with 3D rotations!
Multiplications of this form are called sandwich multiplications, for (I hope) obvious reasons.
OK this is how it works in 2d, and you can stop reading here, knowing that a similar thing occurs in 3d space, though it gets way more complex. If you want to dive into that, keep on reading, but put on your safety helmet first!
Understanding rotations in 3d
Still reading? Safety helmet on? Good. Let’s see if we can also rotate in 3D, by multiplying special numbers.
Spoiler alert: we can.
The first idea, to use special numbers of the form (a+bi+cj) doesn’t work. (Mathematicians have been trying this for quite some time without success…)
The Irish mathematician Sir William Rowan Hamilton (whilst walking along the Royal canal in Dublin, not at all paying attention to what his wife was telling, about how her friend had been wearing this outrageously colored dress at last night’s soiree) discovered that we need special numbers of the form where
where 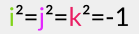 These are what I shall refer to as Hamilton numbers. (Remember that I use that as a sort of euphemism for quaternions; they are not actually called that.)
These are what I shall refer to as Hamilton numbers. (Remember that I use that as a sort of euphemism for quaternions; they are not actually called that.)
Now, imagine a (linked) ‘copy’ of our beloved 3D space. In your mind, place this copy perpendicular to our 3D space (don’t worry if you can’t do this. Maybe you can imagine two paralel 3 dimensional worlds...). We shall call this the imaginary (3 dimensional) world. Every point in our real world has a corresponding point in this imaginary world. And everything that happens in the imaginary world, happens in the real world and vice versa. Just like in the Netflix series Stranger Things!
Here’s a sloppy version of how quaternion rotations work...
Under the hood, Blender takes the vector of rotation, divides it by its length and puts it in the imaginary world, along with the object that needs to be rotated, then rotates the object twice by a multiplication sandwich of Hamilton numbers; the first part of the sandwich creates a Hamilton number with a (usually) non-zero real part, meaning we now have one foot in the real world, while our other three limbs are still in the imaginary world. The second part of the sandwich multiplication makes the real component zero again, so that we are completely back in the imaginary world. Then, Blender puts the rotated object back into the real world (and who’s your uncle?).
By multiplying twice, we also rotated twice (in the same direction!), that is why we need each of those rotations to be half the angle we want the 3D rotation to be.
And although I don’t recommend ever trying to visualize what is happening in more than 3 dimensions, here’s an exclusive ‘behind the scenes’ of what happens when we project the 4 dimensional Hamilton Space onto our 3 dimensional world and make a quaternion rotation of 90° around the (1, 1, 1) vector. Be aware that this is like a 3 dimensional ‘shadow’ of what is happening in 4D; this is not what it would look like in 4D.

In Blender, if we set the rotation mode to quaternion we get the 4 fields: W, X, Y and Z. Important to notice here is, that the angle of rotation is contributing to all four; to be precise, if the angle of rotation is θ, and the unit vector around which we want to rotate is (a, b, c), then:
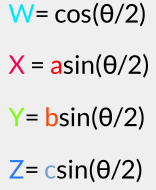
[As we have set 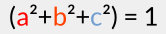 and
and 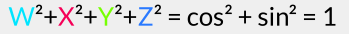
Just to be clear: that rotation vector is placed at the object’s origin. If the object is rotated around some other line, then that is done by rotation around the objects origin AND a translation.
You don't actually have to fill in those fields by hand, but it is good to know what is happening.
Here is some of the math. You also don't need to do this manually, but I think it is a good idea to at least have seen it once. However, if you are feeling brave you can also try this at home! (It looks much more complicated than it actually is)
Getting Stuck into the Numbers: Quartnenions in 3d
As in the case of the complex numbers (...which completely sounds like a lost Sherlock Holmes novel) if we have a Hamilton number then its conjugate is
then its conjugate is 
Furthermore, we will need the following formulas for multiplication;

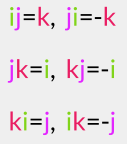
With these rules multiplying any two Hamilton numbers is now super easy (apart from the many terms you need to keep track of...).
There are a few things I would like to point out here:
Let's say we want to multiply above-mentioned Hamilton number h with another Hamilton number p. That is hp, not ph. The order matters here as mentioned above.
So let’s say
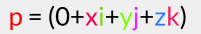
Like I said before, this results in a (usually) non-zero real component, namely:

The imaginary components after this multiplication hp are:
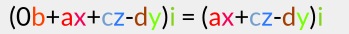
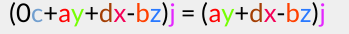
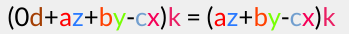
Now we are going to multiply this by the conjugate of 
(So, the total multiplication is: )
)
The resulting real part is now:
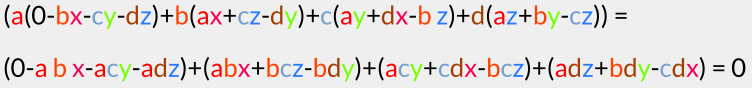
You can see how this works and maybe you can 'feel' how the property 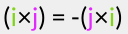 etc. accounts for the fact that ‘left-multiplying’ by h results in the same rotation as ‘right- multiplying’ by h'.
etc. accounts for the fact that ‘left-multiplying’ by h results in the same rotation as ‘right- multiplying’ by h'.
And if you are not convinced, you can carry out the complete sandwich multiplication yourself.
That is why we use half the angle in the rotation. Because we have to multiply twice!
Before you Go: Take-Home Challenge
Your head is probably spinning by now, but I am not completely finished with you just yet; here’s a little challenge:
Open Blender, delete the default Cube, add a Monkey and switch the rotation mode to Quaternion (I know, not much of a challenge yet for most of you, but wait…)
Fill in the W, X, Y, Z fields, so, that Suzanne rotates 180° around the axis that goes through (0, 0, 0) and (3, 4, 5).

Maybe try other angles and axes and, if you feel confident, find the axis and angle when:

And you might want to confirm that:  (or very close to 1, due to rounding errors).
(or very close to 1, due to rounding errors).
That’s all folks! That’s all there is to it. C’est simple comme bonjour. (it’s as simple as ‘hello’)
I hope you more or less ‘get’ quaternion rotations by now and I would like to end with these wise words: the more you think about it, the more sense it will make.

I felt like I was doing pretty good at the start but ended up huddled under a blanket clutching my binky about halfway through.
Which is further than I've reached before trying to understand fancy math so good work! :D
AT LONG LAST! Spikey gives us the nitty-gritty behind the quaternions. This has been a long time coming since his promise to explain it in the forums. And here it is in all of it's glory. Well done spikeyxxx and thank you for all of the hard fought hours put into making this explanation happen. I will go through this tonight in detail but wanted to post my thanks in advance.
spikeyxxx and thank you for all of the hard fought hours put into making this explanation happen. I will go through this tonight in detail but wanted to post my thanks in advance.
aartifact Thank you.
Don't worry too much about not understanding the math: the two main points to take away from this are: 1. a quaternion is just a number.
2. a quaternion rotation is actually a multiplication.
Can't say I understood much of the math. But I CAN say fantastic Job, spikeyxxx
spikeyxxx
After confronting my fears and reading all the math and standing brave amidst all the numbers and melting my brain a little, I can say job well done Spikey.
Thank you, spikeyxxx for this in-depth explanation of "Quaternions" 🙂 and their usage in Blender! Now, I have something to study and try out 😉.
spikeyxxx for this in-depth explanation of "Quaternions" 🙂 and their usage in Blender! Now, I have something to study and try out 😉.